The production steps for industrial test weights may vary depending on the specific manufacturing process and the type of test weights being produced. However, here is a general outline of the production steps involved:
Design and Material Selection: The first step is to determine the design requirements and specifications for the test weights. This includes selecting the appropriate material, such as cast iron, stainless steel, or other materials, based on the desired weight capacity and application.
Material Preparation: The chosen material is prepared for the manufacturing process. This may involve melting and refining the metal in the case of cast iron or stainless steel. The material is then shaped into the desired form, such as ingots or billets.
Molding or Casting: If the test weights are produced using the casting method, the molten metal is poured into pre-designed molds or patterns. The molds are typically made of heat-resistant materials, such as sand or ceramic. The molten metal is allowed to cool and solidify, forming the desired shape of the test weights.
Machining and Finishing: After the test weights are cast or formed, they undergo machining processes to achieve the required dimensions, accuracy, and surface finish. Machining operations may include milling, turning, grinding, and drilling. This step ensures that the test weights meet the specified weight and dimensional tolerances.
Calibration: Once the machining is complete, the test weights go through a calibration process to ensure their accuracy. Calibration involves comparing the actual weight of each test weight with the intended weight using calibrated reference standards. Any deviations or discrepancies are adjusted to bring the test weights within the required accuracy limits.
Surface Treatment and Coating (Optional): Depending on the application and requirements, the test weights may undergo surface treatment or coating processes. This can include sandblasting, painting, powder coating, or applying protective coatings to enhance corrosion resistance, durability, or aesthetics.
Marking and Identification: Test weights are typically marked with relevant information, such as the weight value, accuracy class, serial number, and any necessary certification markings. This allows for easy identification, traceability, and compliance with industry standards.
Quality Control and Testing: Before the test weights are ready for shipment, they undergo rigorous quality control checks and testing to ensure they meet the specified standards. This may involve visual inspections, dimensional measurements, weight verification, and other quality assurance procedures.
Packaging and Shipment: Once the test weights pass all quality control checks, they are packaged appropriately to ensure their protection during transportation. Proper labeling and documentation are also prepared for accurate identification and tracking. The test weights are then shipped to their respective destinations.
Besides,Industrial test weights can be classified based on various factors, including their weight capacity, shape, material, and specific application. Here are some common classifications of industrial test weights:
Weight Capacity:
Standard Test Weights: These are test weights with predetermined and standardized weight values. They are commonly used for calibration and verification purposes and are available in a range of weight capacities, such as 1 kg, 5 kg, 10 kg, and so on.
Custom Test Weights: These are test weights that are specifically manufactured to meet unique weight requirements. They can have non-standard weight capacities and are often used in specialized applications.
Shape and Design:
Cylindrical Test Weights: These are test weights that have a cylindrical shape. They are commonly used in weighing scales and laboratory balances.
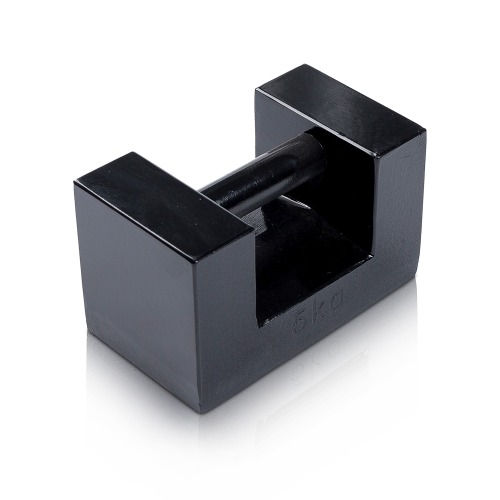
Block Test Weights: These are test weights with a rectangular or block-like shape. They are often used in industrial weighing applications.
Disk Test Weights: These are test weights in the form of flat disks with a circular shape. They are commonly used in laboratory balances and precision weighing instruments.
Material:
Cast Iron Test Weights: These are test weights made from cast iron. They are known for their durability, stability, and high weight capacity.
Stainless Steel Test Weights: These are test weights made from stainless steel. They offer excellent corrosion resistance, durability, and precision.
Brass Test Weights: These are test weights made from brass. They are often used in applications that require non-magnetic properties and high corrosion resistance.
Application:
Industrial Weights: These are test weights designed for industrial applications, such as weighing heavy machinery, tanks, or large-scale industrial processes.
Laboratory Weights: These are test weights specifically designed for laboratory use, such as calibrating laboratory balances, analytical instruments, and precision scales.
Legal Metrology Weights: These are test weights that adhere to specific legal requirements and standards set by regulatory bodies. They are used for commercial transactions, trade, and legal metrology purposes.



 English
English